The Large river floodplain macrogroup consists of the following habitats:
North-Central Appalachian Large River Floodplain

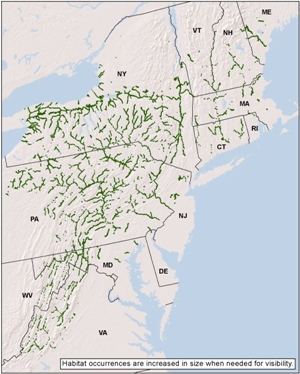
Regional distribution:
CT, DC, DE, MA, MD, ME, NH, NJ, NY, PA, RI, VA, VT, WV. 254,862 total acres of habitat, of which 19.8% is conserved.
Description:
A complex of wetland and upland vegetation on floodplains of medium to large rivers in Atlantic drainages. They are typical of larger rivers but they can occur on smaller rivers where the stream gradient is low and a broad floodplain develops. The vegetation complex includes floodplain forests in which silver maple, sycamore, box elder, and cottonwood are characteristic, as well as herbaceous sloughs, shrub wetlands, ice scours, riverside prairies, and woodlands. Most areas are underwater each spring; microtopography determining how long the various habitats are inundated. Depositional and erosional features may both be present depending on the particular floodplain.
Download the
pdf for this habitat for information about species, crosswalks to state names, and condition of this habitat.
North-Central Interior Large River Floodplain

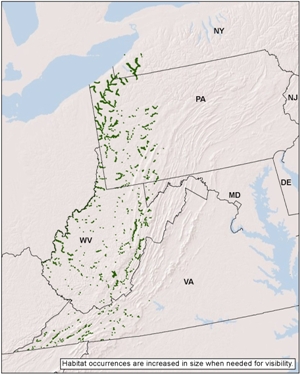
Regional distribution:
MD, NY, PA, VA, WV. 70,068 total acres of habitat, of which 15.6% is conserved.
Description:
A complex of wetland and upland vegetation on floodplains of medium to large rivers in the Ohio River drainages. Vegetation is variable, dominants often include silver maple, sycamore, green ash, American elm, sweet gum, pin oak, and swamp white oak. Understory species are mixed, but include sedges and shrubs such as buttonbush. A single occurrence may extend from river's edge across the outermost extent of the floodplain or to where it meets a wet meadow or upland system. Examples may contain well- drained levees, terraces and stabilized bars, herbaceous sloughs and shrub wetlands. Most areas are inundated at some point each spring; microtopography determines how long the various habitats are inundated.
Download the
pdf for this habitat for information about species, crosswalks to state names, and condition of this habitat.
Laurentian-Acadian Large River Floodplain

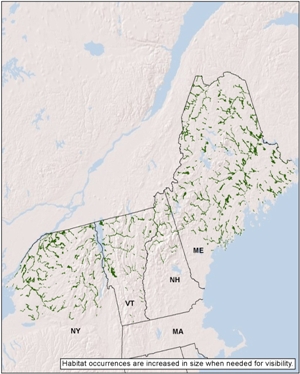
Regional distribution:
ME, NH, NY, VT. 431,558 total acres of habitat, of which 24.5% is conserved.
Description:
A complex of wetland and upland vegetation on floodplains of medium to large rivers in the northeastern US and adjacent Canada, north of the range of sycamore. Vegetation includes silver maple floodplain forests as well as herbaceous sloughs and shrub wetlands. Green ash, American elm, red maple and musclewood are typical associates, and black willow is characteristic of levees adjacent to the channel. On terraces, sugar maple, red oak or ash may be locally prominent. The herb layer includes abundant spring ephemerals, often giving way to fern dominance by mid-summer. In the far north, this system includes ice-scour rivershores dominated by herb and shrubs, and boreal floodplain forests characterized by balsam poplar.
Download the
pdf for this habitat for information about species, crosswalks to state names, and condition of this habitat.
Piedmont-Coastal Plain Large River Floodplain

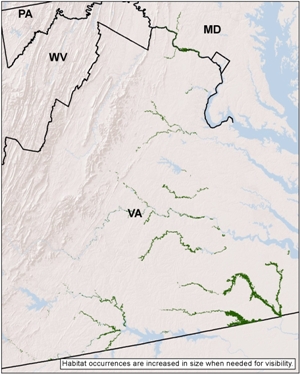
Regional distribution:
MD, VA. 131,403 total acres of habitat, of which 9.3% is conserved.
Description:
A complex of wetland and upland vegetation on floodplains along larger rivers, where temporary to seasonal flooding affects vegetation composition and dynamics. Vegetation includes both non-forested bar and scour communities and a diverse group of more extensive forests. Microtopographic heterogeneity is high, and forests tend to be differentiated by depositional landforms such as levees, sloughs, terraces, and abandoned channels. Better drained soils may support wet site oaks, shagbark hickory, and sweetgum. Wettest swamps are often dominated by green ash and red maple. Bald cypress may occur, but does not dominate. Understories are generally open, with sedges and grasses or moisture-loving forbs in the herb layer.
Download the
pdf for this habitat for information about species, crosswalks to state names, and condition of this habitat.